
Here are today’s most important updates from the realm of Science and Space.
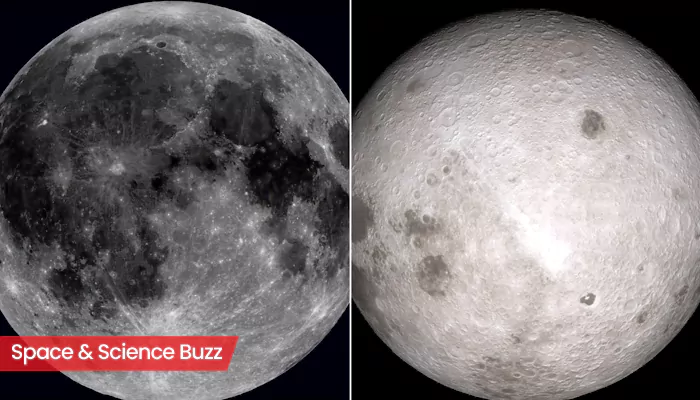
Scientists Unlock Mystery on the Hidden Half of the Moon
The mysterious far side of the Moon may be significantly cooler deep within its interior than the side that permanently faces Earth, according to a new study. The research analysed rock and soil fragments collected in 2024 by Chang’e-6 spacecraft from a vast crater on the Moon’s far side. Using advanced chemical analysis, the team found that the sample, about 2.8 billion years old, crystallised from lava at roughly 1,100C, around 100C cooler than near-side rocks studied from the Apollo missions. The far side, with its thicker crust and rugged, cratered terrain, appears to have been less volcanically active than the near side. Researchers suggest this may be due to a shortage of heat-producing elements, uranium, thorium, and potassium, within its interior. These elements, typically associated with volcanic activity, seem disproportionately concentrated on the near side, where vast basalt plains are visible.
Study Finds Junk Food Can Wreck Memory in Under a Week

Scientists discovered that high-fat junk food disrupts memory circuits in the brain almost immediately. According to the study, there is a special group of brain cells in the hippocampus, called CCK interneurons, become overly active after eating a high-fat diet (HFD), due to an impaired ability of the brain to receive glucose (sugar). This overactivity disrupts how the hippocampus processes memory, even after just a few days of high fat diet. This type of diet resembles typical Western-style junk food rich in saturated fat like cheeseburgers and fries. The discovery also showed that a protein called PKM2, which controls how brain cells use energy, plays a key role in this problem. Restoring glucose calmed the neurons, showing that interventions like fasting or dietary shifts can restore brain health. This could help prevent obesity-related dementia and Alzheimer’s.
New Study Reveals Yoga Isn’t the Heart Hero We Believed

Contrary to widespread belief, yoga may be less effective than conventional forms of exercise in enhancing vascular health, according to a new study. Sedentary behavior and prolonged sitting are known to impair vascular function, increasing the risk of hypertension, cholesterol buildup, and thrombosis. The researchers conclude that traditional exercise modalities, such as Tai Chi, Pilates, and high-intensity interval training, consistently outperform yoga in improving vascular function among sedentary individuals. While yoga remains accessible and culturally significant, the study suggests that individuals seeking consistent cardiovascular benefits may need to supplement yoga with more vigorous forms of exercise.
From Garden to Gums: Plant-Based Compound Targets Oral Disease

A powder based on morin, a natural compound extracted from plants such as guava leaves, apple and fig peels, certain teas, and almonds, has shown antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects against bacteria that cause periodontal disease. It is expected that the substance, released in a controlled manner through polymers, will help with nonsurgical treatments as an alternative to antibiotics for controlling microorganisms. Morin is a flavonoid that can be obtained from various fruits. But simply eating it isn't enough; the substance needs to be processed. The idea is to take advantage of this natural compound, its benefits, and its advantages, and transform it all so that it can be used to prevent and treat tooth decay and periodontal disease, as revealed by researchers.




.webp)
.WEBP)
.WEBP)
.webp)
.webp)


.webp)